
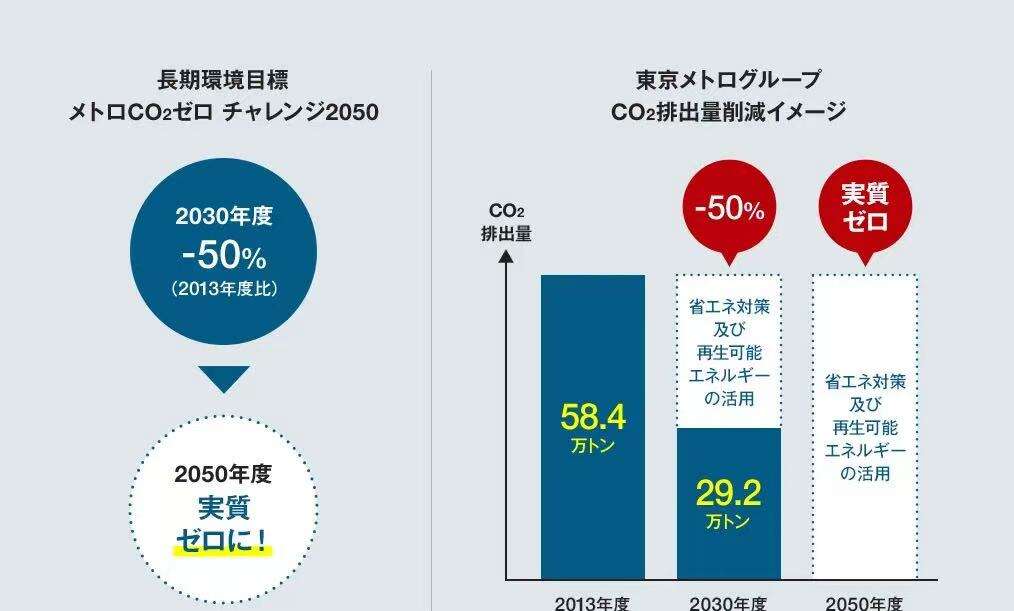
To achieve decarbonization and a circular society, Tokyo Metro has set the "Subway CO₂ Zero Challenge 2050" goal, aiming to reduce CO₂ emissions to virtually zero by fiscal 2050. Developing a more energy-efficient vehicle drive system is an urgent task at present.
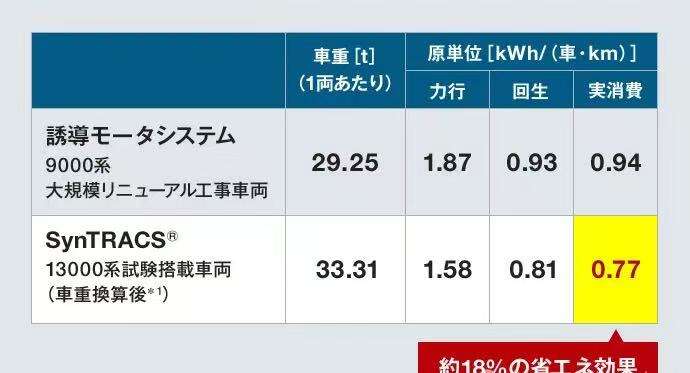
Tokyo Metro collaborated with Mitsubishi Electric to install a synchronous reluctance motor system on trains. From 2021 to 2022, it became the first in the world to confirm through commercial operation that the system can achieve approximately 18% energy savings (compared based on the weight conversion of the 9000 series large-scale renewal project vehicles). The project originated from a proposal by Mitsubishi Electric. At a regular seminar where Tokyo Metro discussed energy-saving optimization of railway vehicle drive systems (including control devices) with multiple manufacturers, Mitsubishi Electric proposed equipping a synchronous reluctance motor system with SiC-based VVVF inverters (control devices) to pursue further energy savings. Though applying this motor to railway vehicles was unprecedented globally with uncertainties, Tokyo Metro decided to launch this world-first system development project, driven by its willingness to explore new technologies and trust in Mitsubishi Electric's past achievements.
