This article lists Japan's five major railway vehicle manufacturers and their market shares at home and abroad, analyzing the structure of body-integrated companies covering Shinkansen, traditional commuter trains and subways from the perspective of market size.
1. Hitachi, Ltd.
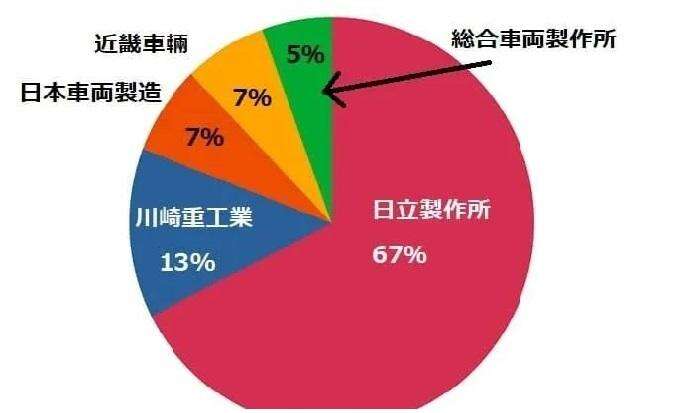
Hitachi supplies vehicles to Japan's JR and private railways, with a domestic market share of about 30%. Relying on its global sales network, its annual sales in the railway sector reach 630 billion yen. After acquiring the railway division of Italy's Finmeccanica Group in 2015, it joined the ranks of the world's top railway vehicle manufacturers. In recent years, it has achieved rapid growth, and its performance in the railway sector is particularly prominent compared with other sectors such as information and communications and electronic devices (with sales of only about 160 billion yen in 2014).
2. Kawasaki Heavy Industries
Kawasaki Heavy Industries takes the leading share in Japan's Shinkansen vehicle orders and manufactures various vehicles for JR and private railways' conventional lines, ranking top domestically. However, in the overseas market, there is a significant gap with Hitachi, with fewer orders for high-speed railways, commuter trains and subways. Due to disadvantages in price and delivery time compared with other international manufacturers, overseas sales growth is weak. In 2017 and 2018, its railway division even fell into deficit, mainly relying on profits from other fields such as aerospace, precision machinery and robots to maintain overall profitability, in sharp contrast to Hitachi's substantial profits.
3. Nippon Sharyo
As a subsidiary of the JR Central Group, Nippon Sharyo is famous for producing N700 series vehicles for the Tokaido, Sanyo and Kyushu Shinkansen. It also undertakes orders from JR and private railways for conventional lines, ranking third among domestic manufacturers with a market share of about 20%-30%. However, affected by the slow progress of Japan's Shinkansen exports, its global market share is low, and its future industry status will largely depend on the overseas expansion results of JR Central's Shinkansen.
4. Kinki Sharyo
Affiliated to the Kintetsu Group (with JR West Japan participating in investment), Kinki Sharyo is an important railway vehicle manufacturer in the Kansai region centered on Osaka. In addition to Kintetsu, it also undertakes vehicle manufacturing for Tokyo Metro, some JR and private railways. Its overseas market scale is still small, and its business focus remains domestic, ranking fourth in Japan's railway-related sales.
5. Japan Transport Engineering Company (J-TREC)
A subsidiary of the JR East Group, J-TREC mainly undertakes orders for conventional line vehicles from JR East and manufactures vehicles for some private railways in the Tokyo metropolitan area, but with few deliveries outside the metropolitan area. It has a small share both in the domestic and global markets, ranking fifth in Japan's railway vehicle and related business sales.
6. Two Camps of Japanese Railway Vehicle Manufacturers
Japanese railway vehicle manufacturers can be divided into "heavy industry series" and "railway company series", neither of which focuses solely on railway vehicles; vehicle manufacturing is only part of their multiple departments or affiliated companies' businesses. The heavy industry series, represented by Hitachi and Kawasaki Heavy Industries, are comprehensive electrical manufacturers involving aerospace, precision machinery, electronic components, industrial robots, information and communications and other fields. Although railway vehicles are an important business, their sales are not far ahead of other departments, different from the model of automobile manufacturers mainly engaged in vehicle manufacturing. The railway company series include Nippon Sharyo, Kinki Sharyo and J-TREC, all subsidiaries (group companies) of large railway operators, affiliated to JR Central, Kintetsu & JR West Japan, and JR East respectively. Their parent companies' core businesses are railway operation, real estate, hotels, in-station commerce, etc.,
